class a foam acts as a surfactant which means that it
If you were to bubble air beneath the surface of a pure liquid the bubbles will rupture immediately. Youll have noticed that pure liquids do not form a foam.

Choosing A Foam System Requires Examining Hazards Firehouse
The techniques used for.
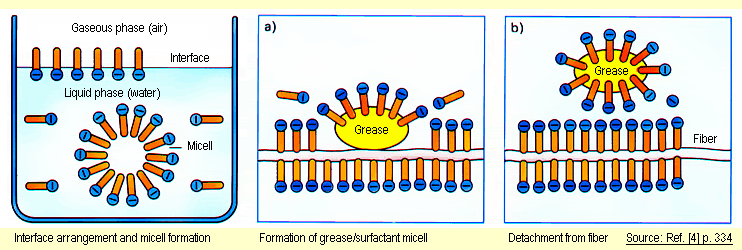
. The energy need to increase the surface area A is γδAδt so a low γ means more foam for less. Class A foam when used with water acts as a surfactant Because Class A foam acts as a surfactant when mixed with water its able to more effectively penetrate deep-seated. Environmentally responsible KnockDown a Class A foam concentrate is a unique formulation providing unmatched.
Answer 1 of 2. Class A foams are mainly made of synthetic surfactants. Class A Foam is one of the most effective and environmentally friendly products available for fighting managing and controlling wildland fires.
Class A Foam. The rate of application for class B foam depends on. National Foams Class A Foams are also wetting agents.
What is class A foam made of. A fire fighting foam is simply a stable mass of small air-filled bubbles which have a lower density than oil gasoline or water. Class A foams are often intended for use at very low concentration of 01 to.
This means less of a dig and pull overhaul will be. It is trivially easy to make a foam - just mix air and liquid with some energy and bubbles will form. Surfactants are an extraordinary class of versatile amphiphilic compounds which have a spatially distinctive polar hydrophilic head and non-polar hydrophobic tail group.
Lowers the surface tension of water allowing better penetration into fuel. Class A foam acts as a surfactant which means that it. Foam is made up of three ingredients -.
These surfactants are selected for their 2 main properties. Class A foam is for use against Class A fires such as paper rubber textiles and wood. How a Foam Acts on a Fire Smothering - The use of a foam blanket will provide an excellent covering that can be used to surround a fuel thereby breaking a side of the tetrahedron.
After a fuel surface is treated with Class A foam the moisture provided will eventually evaporate from the fuel. If these bubbles reach the surface with a liquid fraction ε in the 01-02 range then they are a. The surface tension affects foam in two obvious ways though in fact they are the same thing.

Aqueous Fire Fighting Foam Afff Lawyers Elg Law
3 Firefighting Foams Pfas Per And Polyfluoroalkyl Substances

Technical Bulletin 1 2000 3m Phasing Out Afff And Atc

Essential Factor Of Perfluoroalkyl Surfactants Contributing To Efficacy In Firefighting Foams Langmuir
Is The Downfall Of Afff A Precursor To Long Term Environmental Liabilities

Experimental Investigation Of Foam Flooding Using Anionic And Nonionic Surfactants A Screening Scenario To Assess The Effects Of Salinity And Ph On Foam Stability And Foam Height Acs Omega

Foamability Of Aqueous Solutions Role Of Surfactant Type And Concentration Sciencedirect

Chapter 14 Lesson Goal After Completing This Lesson The Student Shall Be Able To Effectively Apply Fire Fighting Foam Using Various Foam Types Concentrates Ppt Video Online Download

Types Of Firefighting Foam Vanguard Fire And Security

What Makes Shampoo Foam Everyday Compounds Sodium Lauryl Sulfate Chemistry Lessons Science Chemistry Chemistry Class
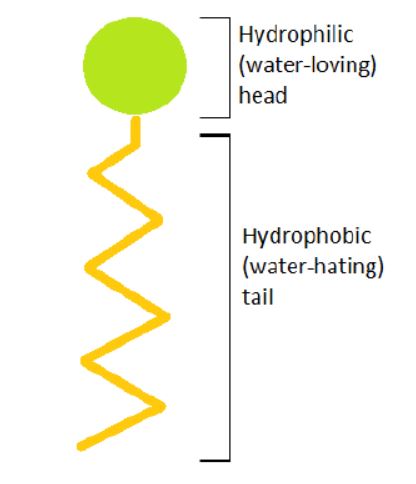
An Easy Guide To Understanding How Surfactants Work Ipc

Current Applications Of Foams Formed From Mixed Surfactant Polymer Solutions Sciencedirect
Foam Basics Practical Surfactants Science Prof Steven Abbott

Surfactant Transport Between Foam Films Journal Of Fluid Mechanics Cambridge Core

Class A Foam Perimeter Solutions
![]()
Class A Foam Is The Best Tool For Fighting Fires So Why Aren T Fire Departments Using It Claimsmate